EDITORIAL TEAM: Carolina Rojas, E4C Expert Fellow; Mariela Machado, E4C Program Manager; Grace Burleson, E4C Research Manager
PARTNER COLLABORATOR: Oslene Carrington, Guyana Economic Development Trust
Click here to view the full report.
The crucial role of agriculture, and agricultural-related activities in the economic development of emerging economies has been widely acknowledged. According to the FAO, by 2009, the share of agriculture in GDP in emerging economies was higher than 30% in Africa, higher than 15% in Latin America, and even higher than 20% specifically within Guyana. Even in developed countries, agriculture can be an important driver of growth, both in terms of income generation and employment opportunity. There is also evidence that agricultural productivity is directly linked to industrialisation levels and the country’s economic growth.
The potential of the agricultural sector in boosting development not only resides on the economic aspects, but also the fact that it contributes to poverty reduction, food and nutrition security, and the sustainable use of natural resources. Historically, low and middle income countries often produce and export low value-added primary agricultural commodities. However, during the last decades, governments and organizations in emerging economies have been promoting the industrialisation of the agricultural sector. Agro-industries, which comprise all the post-harvest activities carried out for the transformation, preservation and preparation of agricultural production for intermediate or final consumption, play a major role in economic growth and poverty reduction by the generation and enhancement of value chains starting from the agricultural primary produce.
The aim of this Research Collaboration is to provide a general perspective of the current trends regarding sustainable development of agroindustries in emerging economies, with recommendations for applying these frameworks to the context of Guyana. This work, developed in partnership with the Guyana Economic Development Trust, explores in a broad manner the ecosystem of strategies and technologies available for supporting the growth of micro and small agro-processing entrepreneurs. The research is supported by detailed desk research on the agricultural sector, interviews with experts of varied backgrounds and interviews with micro and small entrepreneurs of the Guyanese agro-processing sector.
The structure of the report is as follows: First, the general structure of agricultural value chains is presented, highlighting the relevance of considering all the stakeholders involved from farm to fork in order to achieve high quality products, and an efficient allocation of primary resources and benefits for all the parts. Next, the role of energy supply and the need for adopting sustainable technologies for the agricultural sector throughout the entire value chain is discussed. Further, the relevance of food packaging and the main challenges faced by micro and small entrepreneurs regarding packaging of their products is discussed. Additionally, the current trends on packaging types together with the need for transitioning to more sustainable packaging technologies are also presented. Finally, inclusive strategies of packaging industries in order to address the micro and small entrepreneurs’ needs, making use of R&D&I and technology transfer are shown, exemplified with case studies. Importantly, the Guyanese agro-processing environment is discussed and the application of strategies and technologies shown in previous sections is illustrated with a case study. A set of recommendations for the sustainable development of agro-processing industries in Guyana is given, together with a SWOT analysis considering the variables affecting the current Guyanese landscape.
Sweet potato flour value chain in Guyana, with different energy, water and fuel input requirements: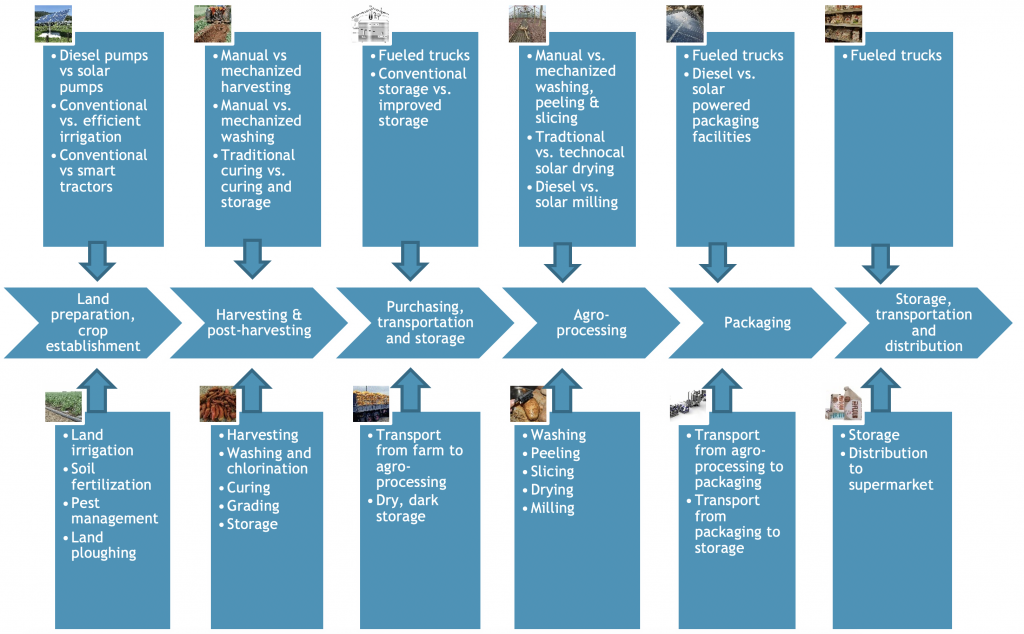
Click here to view the full report.
