Mobile farms, aerial imaging and unmanned helicopters are saving lives as leading edge technology in humanitarian missions. Aerospace engineering is not often the first thought to come to mind when disaster strikes, but that may be changing. These are eight aerospace technologies that are put to use to improve life on the ground.
Mobile Plant Cultivation Unit (MEPA)
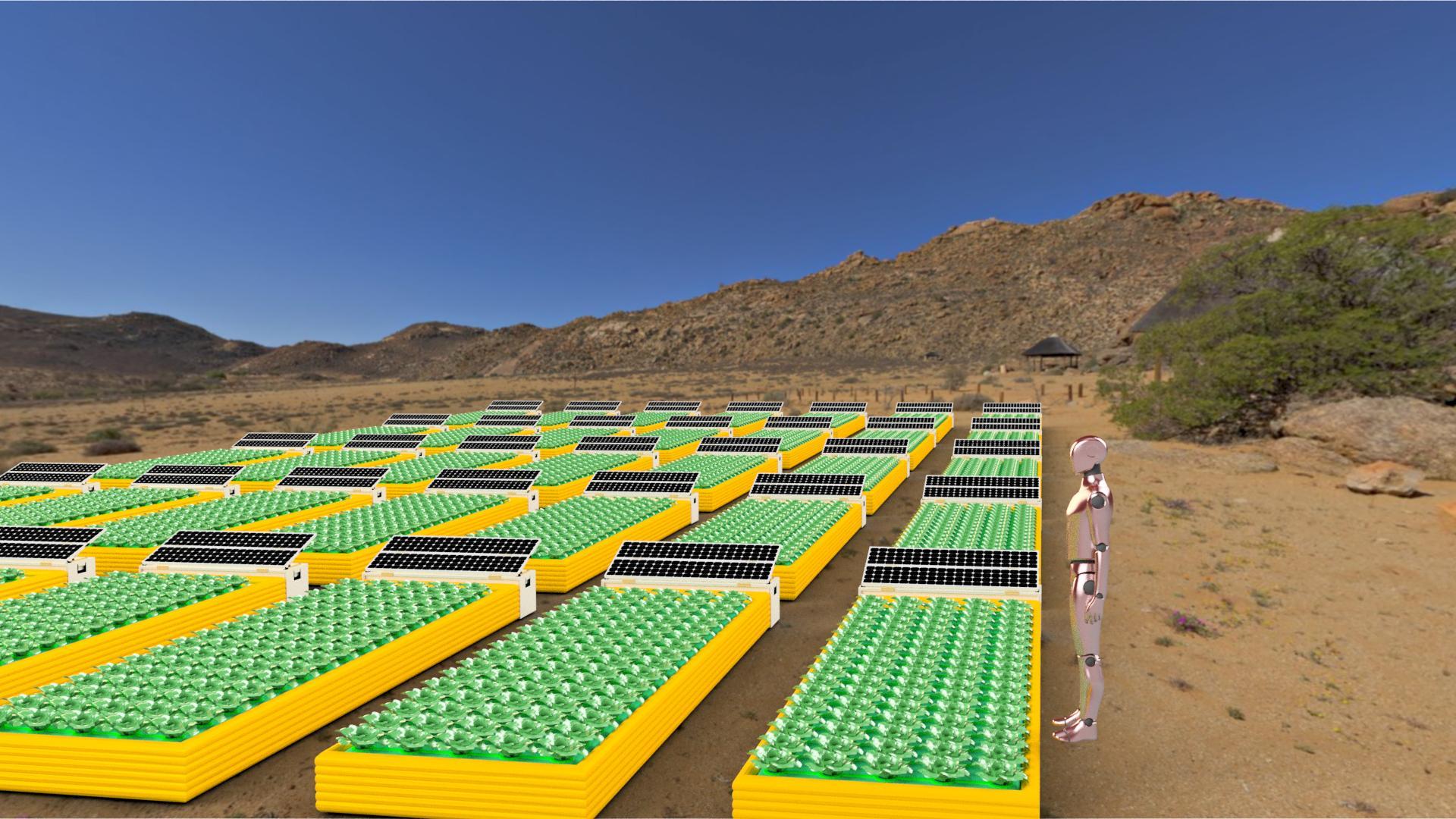

Photo: German Aerospace Center (DLR) (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0)
The Mobile Plant Cultivation Unit was created by the German Aerospace Center (DLR) and the goal of this unit is to eventually send it to space to provide food to astronauts and people living on mars. In the meantime, these units are being used to provide fresh fruits and vegetables in natural disasters and to refugee camps around the globe. These use no soil, are reusable, and are rapid, as they produce a harvest in four to six weeks.
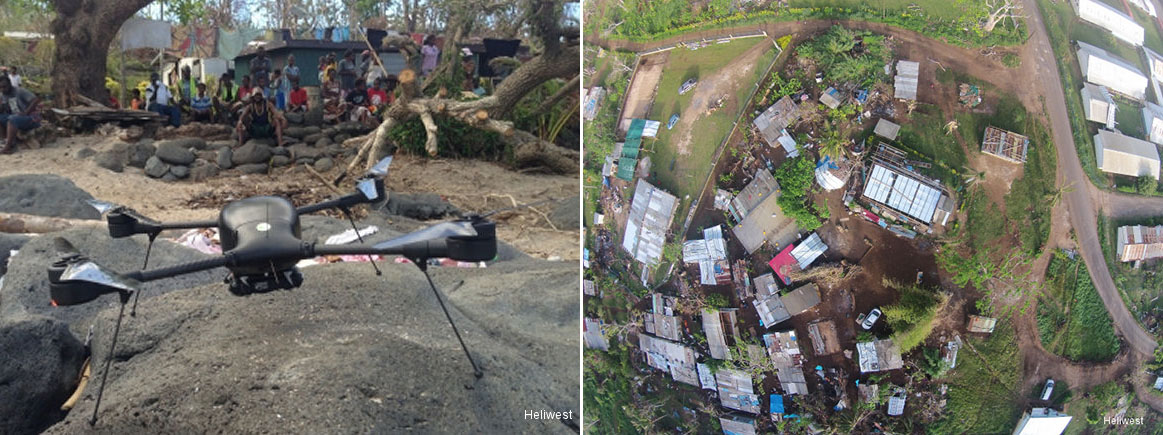
Indago Unmanned Aerial System (UAS)
Lockheed Martin’s unmanned aerial system (UAS) Indago is used in natural disasters to quickly get to hard-to-reach areas and assess damage, as well as search for survivors. In 2015, following a devestating cyclone in Vanuatu, the Vanuatu government and World Bank called on Heliwest, an Australian UAS operator, to deploy these systems to navigate the destruction and provide an accurate picture of damaged property and assets.
NASA Satellite Combating Cholera
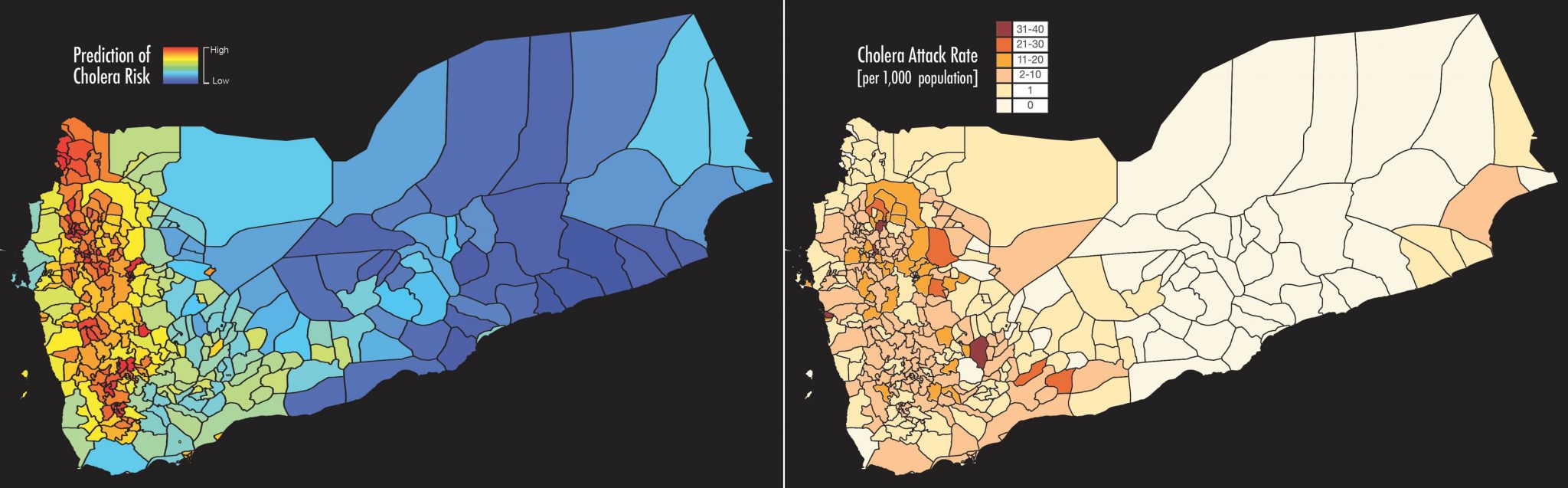
Left: Predicted cholera risk based on analysis and satellite data in Yemen, June 2017. Blue indicates low risk of cholera, red indicates high risk. Right: The actual number of cholera cases in June 2017. The red area represents reported cholera cases. Images: West Virginia University/Antar Jutla via NASA
NASA used a satellite to assess environmental conditions from space and predicting which regions of Yemen have the highest cholera risk. They collaborated with people on the ground in Yemen, where the disease is a huge health threat. This resulted in predicting where the cholera outbreaks would occur and saved many lives.
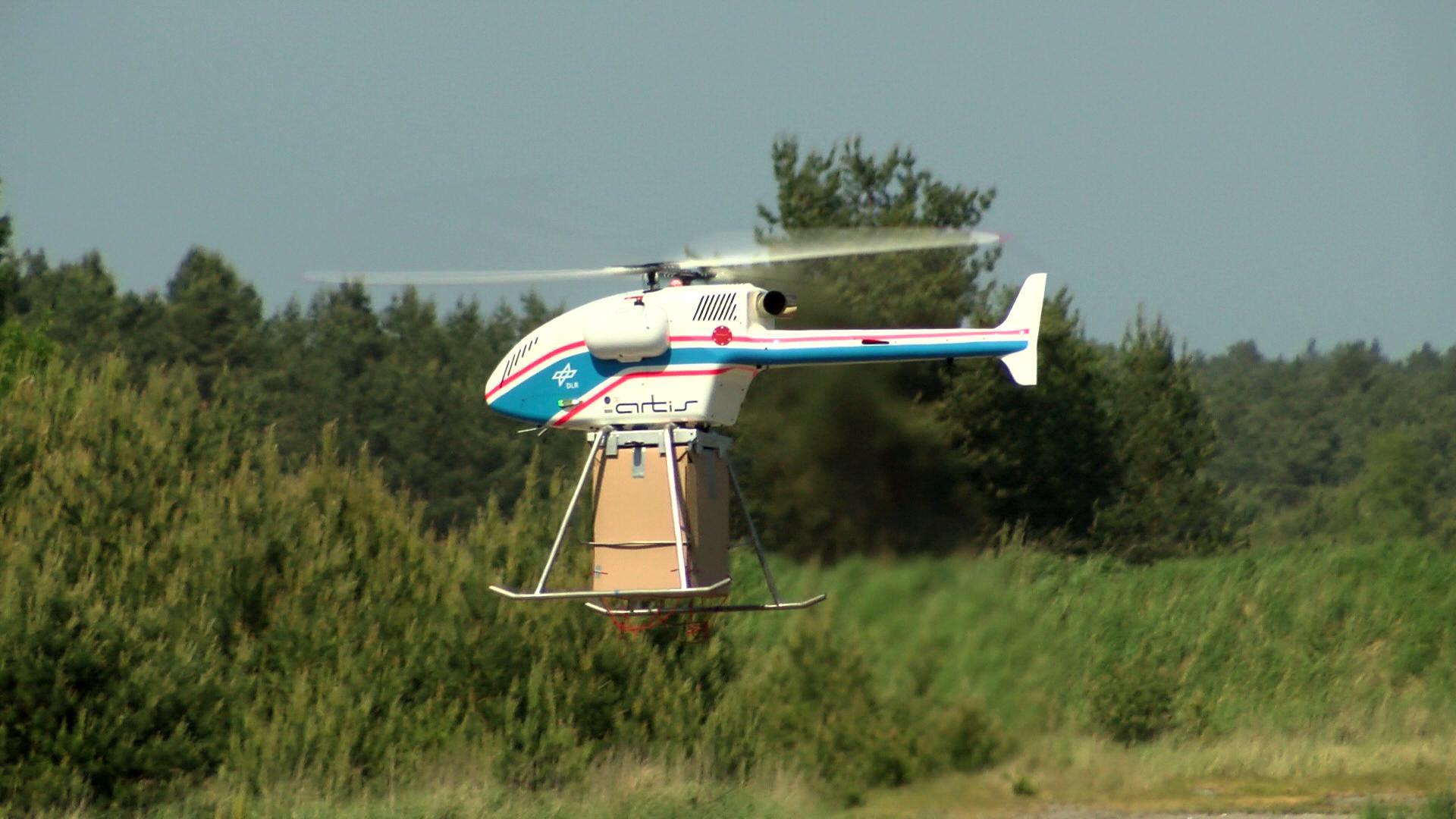
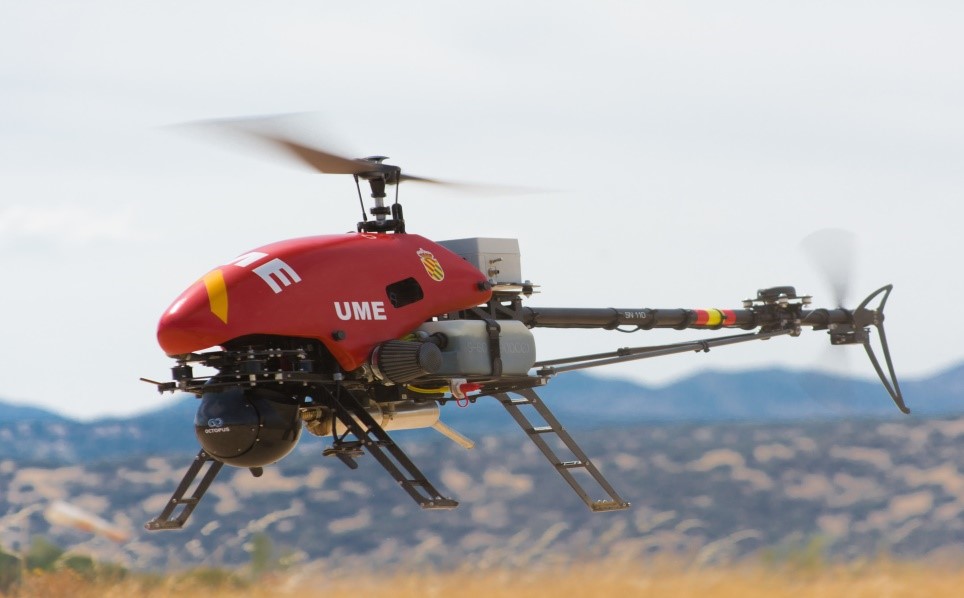
SuperARTIS Helicopter
SuperARTIS is a small, unmanned helicopter operated by the German Aerospace Center that can transport payloads of up to 30 kilograms. This technology can get to remote or inaccessible locations to transport aid supplies during disaster or other times of need.
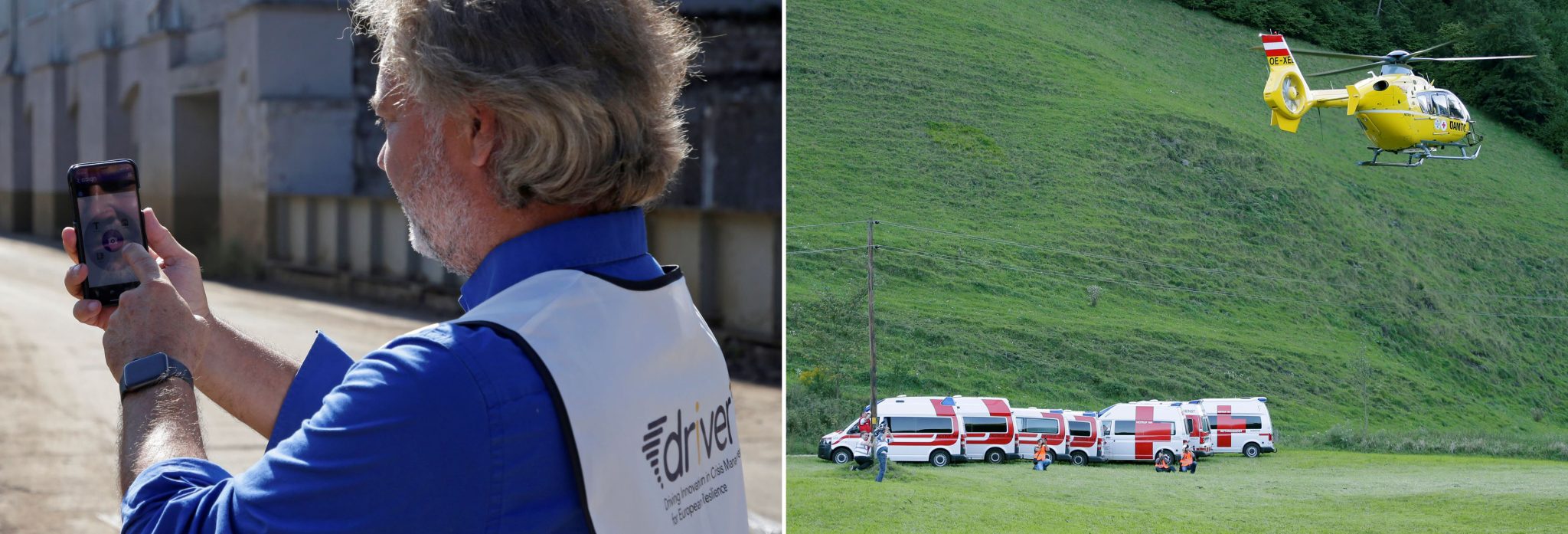
DRIVER+ (Driving Innovation in Crisis Management for European Resilience)
This technology is an aerial imaging system developed and used in Europe. The system aids responders during disasters, such as fires or floods. Aerial systems fly over affected regions and capture images so that relief workers can get a sense of what is happening and where to go.
ReponDrone
This is an international project co-funded by the European Union (EU) and the Korean government. This is a fleet of drones that will allow a small team to operate all the drones at once, improving human resources, and will be able to be used by first responders. The goal is to be able to respond to disaster more quickly and efficiently, and deliver information about the situation to anyone who needs it in real time.
Data4Human
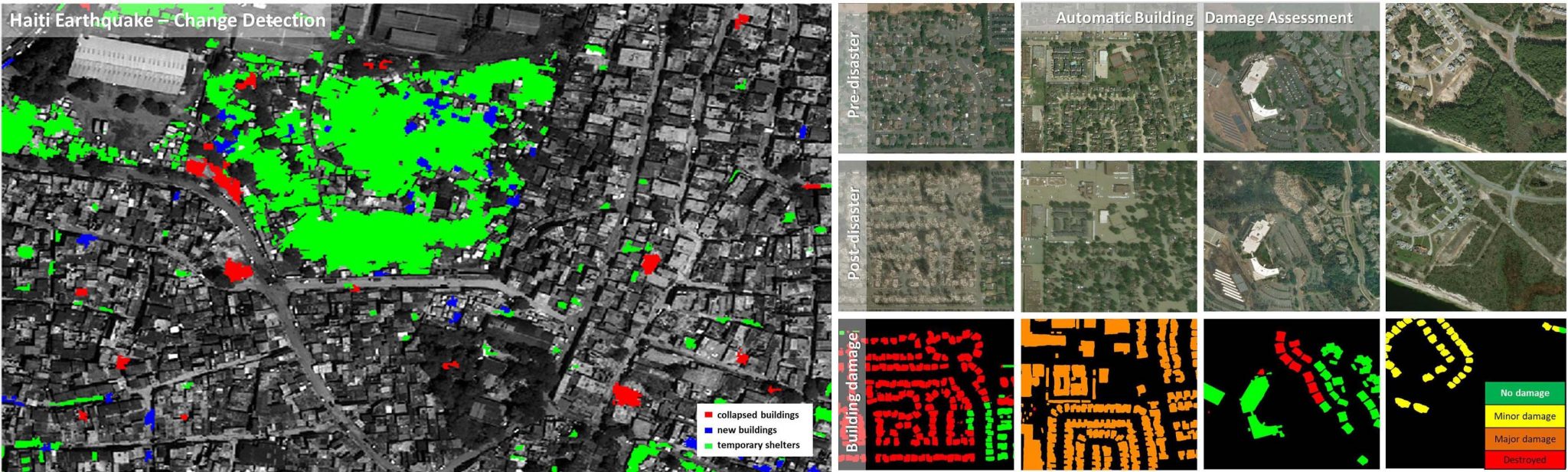
These images show Data4Human analyzing aerial photos to assess damage. Photo: German Aerospace Center (DLR) (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0)
This technology uses data acquired by satellites in order to make decisions on certain situations and disasters. Projects that use this technology include monitoring the marine environment, mapping urban areas, developing warning systems for climate change, obtaining data on agriculture and crop losses, and many others. The goal is to be able to obtain more data for humanitarian efforts to act quickly and have information on location and specifics.
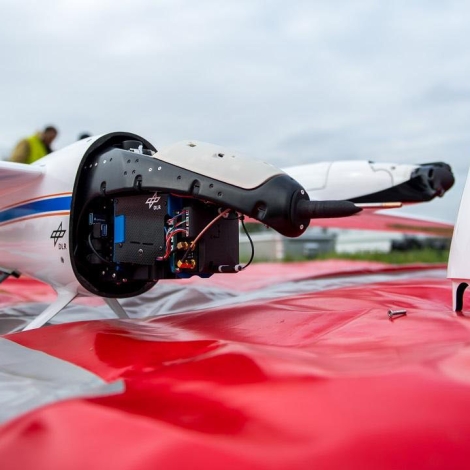
Drones4Good
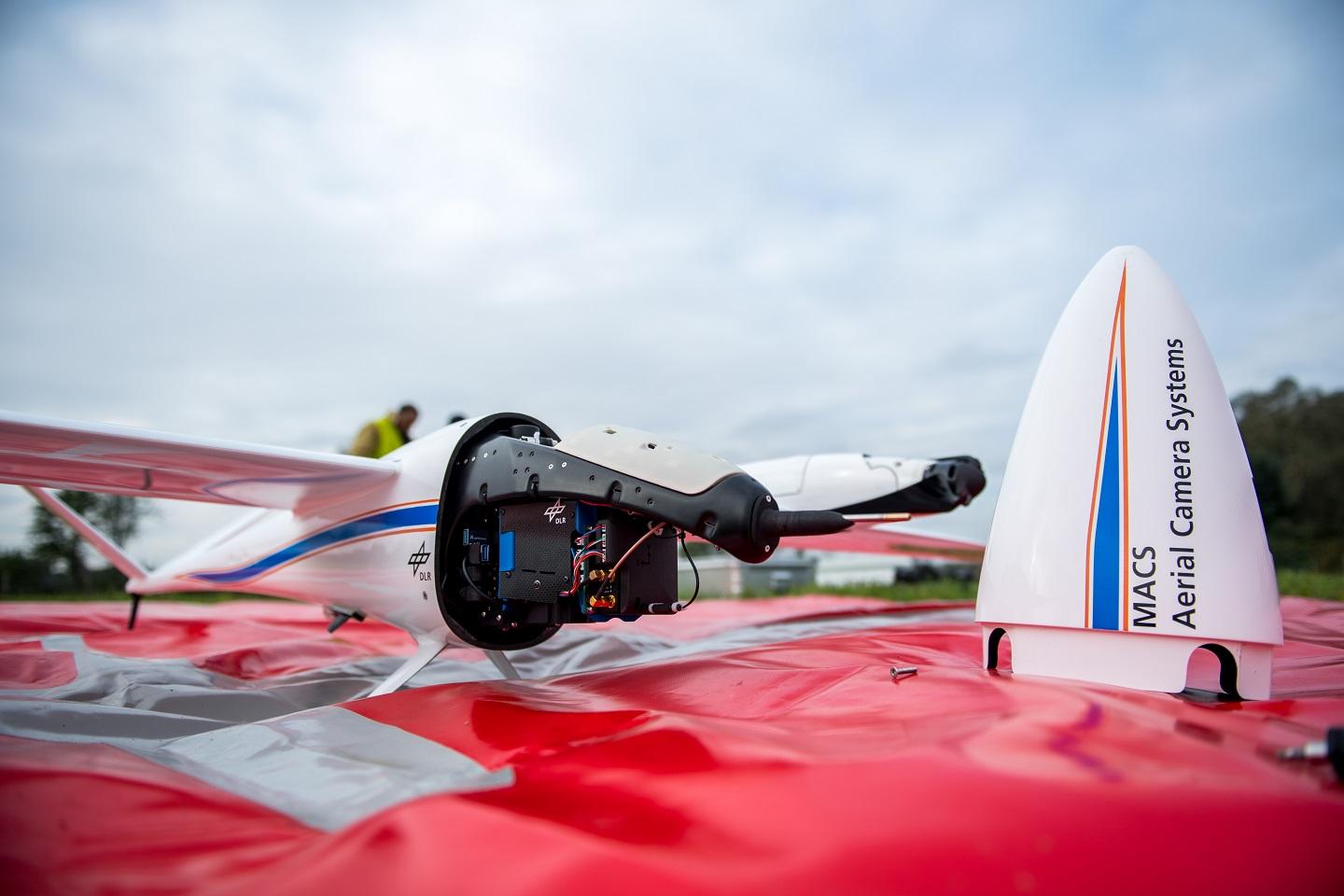

The drone with an integrated modular aerial camera system is part of the Drones4Good program. Photo: German Aerospace Center (DLR) (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0)
This drone technology uses Artificial Intelligence (AI) in order to quickly collect and analyze large amounts of data for humanitarian relief efforts. The drone is able to take aerial images and get to inaccessible areas quickly and efficiently. This allows for relief to get to disaster and crisis areas in order to help.





