Digital Toolkits for Enhancing Flood and Extreme Heat Resilience of Low-income Housing
This project assessed the application of digital toolkits to enhance awareness and uptake of recommendations on design, materials, and strategies for flood and extreme heat-resilient housing among community members in Florida and Pennsylvania in the United States. The specific areas of focus include low-income housing, sustainable materials, vulnerable housing retrofit measures, climate change responsive design strategies, and toolkits for resilient design solutions.
The objectives were:
- Assess the current housing needs for communities exposed to flooding and extreme heat in Florida and Pennsylvania
- Identify the most commonly used materials, technologies, and engineering design strategies for flooding and extreme heat resilience.
- Review existing toolkits for disseminating information on housing risks and potential improvement for communities in vulnerable areas of Florida and Pennsylvania.
- Determine the gaps in knowledge dissemination for existing engineering solutions for climate change resilience of low-income housing.
- Develop a conceptual framework for a digital co-learning platform that can be used by community members to access information on solutions for resilient housing in Florida and Pennsylvania.
An in-depth review of related literature through desk research coupled with stakeholder brainstorming sessions and subject matter interviews provided a roadmap that shaped the outcomes of this study. The resilience of low-income housing relies on a holistic approach to the development of design solutions, materials, and strategies that promote flood and extreme heat mitigation. Dissemination of these solutions through digital toolkits that are easily accessible to communities in vulnerable areas enhances the uptake of solutions and creates awareness of flood and heat risks.
Existing toolkits are limited in their accessibility and efficiency due to the siloed and top-down development and limited contextual focus. Integration of these toolkits can enhance their use by the stakeholders within the flood and extreme heat risk reduction within Florida and Pennsylvania. This research provides a proposal for an information and knowledge collating platform that can integrate, filter, and simplify flood and extreme heat risks or solutions for the different stakeholders.
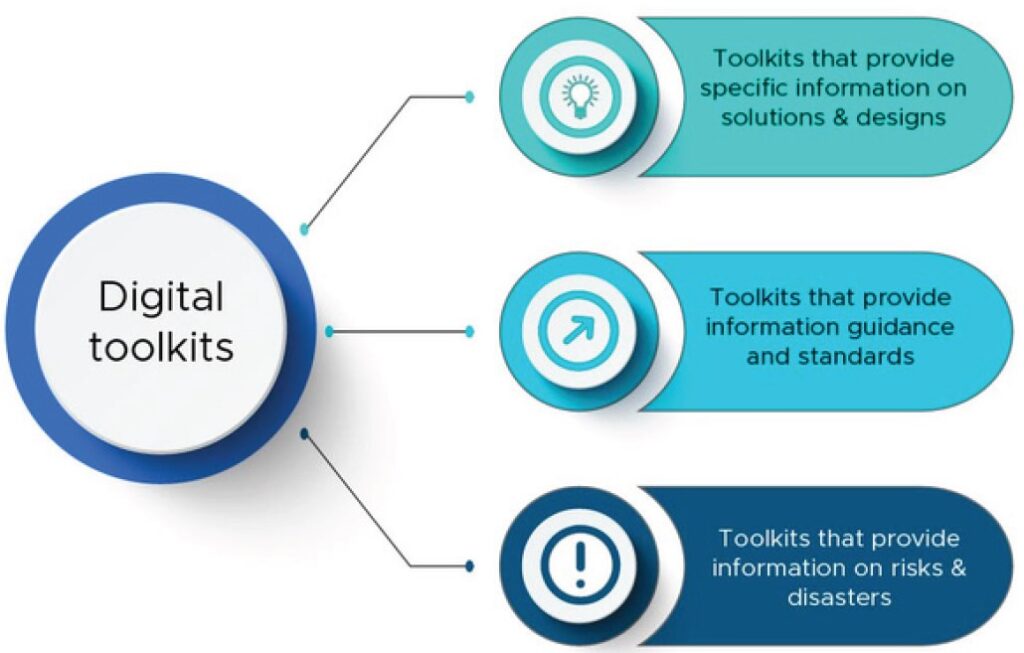
Types of digital toolkits used for disaster risk awareness and resilience approaches in the housing sector
