
Agriculture
June 23, 2024
Q Drum
Read SolutionImplemented by
Hans Hendrikse and Pieter Hendrisikse (Q Drum)
Updated on January 11, 2024
·Created on September 26, 2019
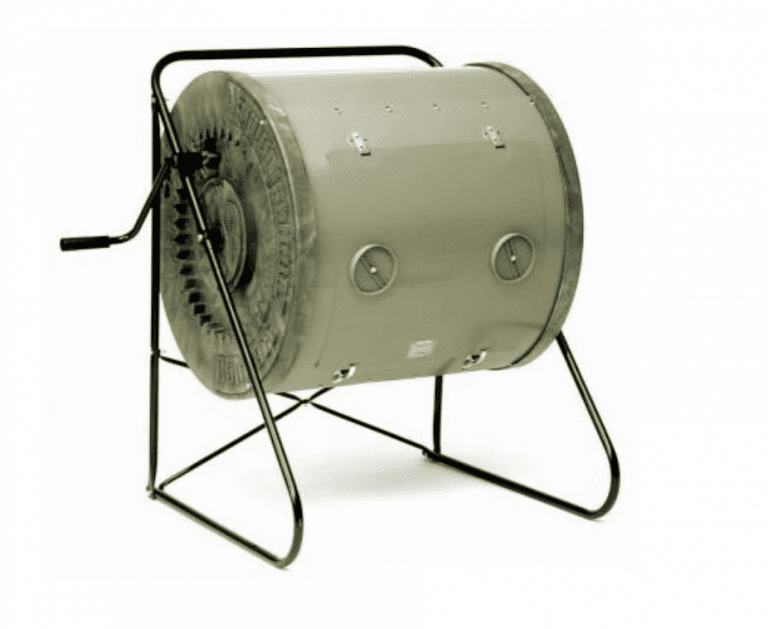
The rotary drum composter uses large amounts of ventilation to reduce composting time to 2–3 weeks.
Target SDGs
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
Market Suggested Retail Price
$300.00
Target Users (Target Impact Group)
Household, Community, Small and Medium-sized Enterprises, Public Sector Agencies
Distributors / Implementing Organizations
This product is available at retailers in India and in the USA.
Competitive Landscape
Direct competitors include Vermicomposting and NADEP Composting.
Regions
Worldwide
Manufacturing/Building Method
Manufactured by a number of distributors
Intellectural Property Type
Open-source
User Provision Model
Users obtain the product from different distributors.
Distributions to Date Status
Unknown
Input requirement (volume and frequency)
25 kg cow dung, 20 kg mixed vegetable waste, 10 kg saw dust, 5 kg compost (bulking agent), 1 time/20 days.
Additives
Saw dust, compost (bulking agent)
Production capacity (kg output per kg input)
~42 kg output per 60 kg input
Production duration
2-3 weeks
Percentage of nutrient recovery
2.1% nitrogen and 3.5% total phosphorus
Complementary treatment needed
None
Design Specifications
Rotary drum sizes my vary, but one study of a rotary drum composter used a 250 L capacity drum of 0.92 m in length and 0.9 m in diameter, made up of a 4 mm thick metal sheet. The inner side of the drum was covered by anti-corrosive coating and mounted on four rubber rollers attached to a metal stand. The drum is rotated manually.
40 mm angles are welded longitudinally inside the drum to mix the wastes, and two holes drain excess water. Waste should be shredded and placed inside at 70% of the total volume, with both half side doors of the drum open to allow additional aeration. Initial moisture content was around 61% and the cattle manure, mixed green vegetables and sawdust entered in a 2.5 : 2 : 1 ratio, on wet mass basis.
Technical Support
There is no technical support provided and users are expected to maintain the product on their own.
Replacement Components
None
Lifecycle
Unknown
Manufacturer Specified Performance Parameters
Rapid compost time of 2-3 weeks, pathogen inactivation, nutrient rich fertilizer.
Vetted Performance Status
The rotary drum composter was assessed for temperature, C/N ratio, TOC, coliforms, metals, turning frequency, and nutrient retention.
Safety
Implementers must take appropriate precautions when working with organic waste, particularly cattle manure, and ensure complete decomposition.
Complementary Technical Systems
None
Academic Research and References
Kalamdhad, A.S., Kazmi, A.A., 2008, Mixed Organic Waste Composting Using Rotary Drum Composter. International Journal of Environment and Waste Management, 2, pp. 24-36.
Kalamdhad, A.S., et al., 2009, Rotary drum composting of vegetable waste and tree leaves. Bioresource Technology, 100, pp. 6442-6450.
Kalamdhad, A.S., et al., 2008, Stability evaluation of compost by respiration techniques in a rotary drum composter. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 52, pp. 829-834.
Villasenor, J., et al., 2011, Composting domestic sewage sludge with natural zeolites in a rotary drum reactor. Bioresource Technology, 102, pp. 1447-1454.
Singh, J., Kalamdhad, A.S., 2013, Assessment of bioavailability and leachability of heavy metals during rotary drum composting of green waste (Water hyacinth). Ecological Engineering, 52, pp. 59-69.
Kalamdhad, A.S., Kazmi, A.A., 2009, Effects of turning frequency on compost stability and some chemical characteristics in a rotary drum composter. Chemosphere, 74, pp. 1327-1334.
Varma, V.S., Kalamdhad, A.S., 2015, Evolution of chemical and biological characterization during thermophilic composting of vegetable waste using rotary drum composter. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 12, pp. 2015-2024.
Compliance with regulations
Unknown
Evaluation methods
The rotary drum composter was assessed for temperature, C/N ratio, TOC, coliforms, and nutrient retention.
Other Information
Open source designs are available.

Agriculture
June 23, 2024
Implemented by
Hans Hendrikse and Pieter Hendrisikse (Q Drum)

Agriculture
January 17, 2024
Implemented by
Philippine Army

Agriculture
January 2, 2024
Implemented by
Toilets for People

Agriculture
August 13, 2024
Implemented by
Sun-Mar

Agriculture
December 18, 2023
Implemented by
Clivus Multrum

Agriculture
January 17, 2024
Implemented by
Narayan Deotao Pandharipande

Agriculture
August 16, 2024
Implemented by
EcoSwell

Agriculture
August 8, 2024
Implemented by
Patrick Kiruki, Banza Sanitation

Agriculture
February 4, 2024
Implemented by
Dhaara Smart

Agriculture
August 17, 2024
Implemented by
Roboterr Sewarage Construction
Have thoughts on how we can improve?
Give Us Feedback