
Agriculture
August 15, 2024
Struvite Reactor Tank
Read SolutionImplemented by
EAWAG
Updated on January 11, 2024
·Created on October 1, 2018
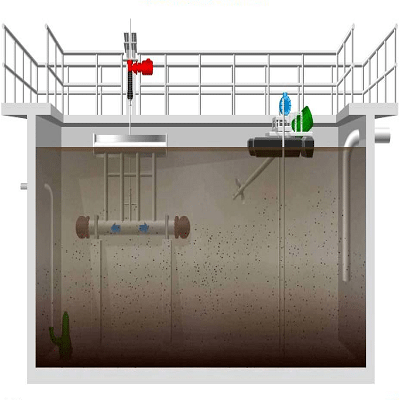
Sequential Batch Reactors (SBR) are aerobic wastewater treatment systems using activated sludge processes.
Sequential Batch Reactors (SBR) are wastewater treatment systems which employ suspended-growth processes. These processes are achieved through injecting oxygen to both maintain aerobic conditions and mix the wastewater, which activates sludge. Activated sludge systems remove organic matter, nutrients, biochemical oxygen demand, and chemical oxygen demand. However pathogen removal is low. The treated water can either be inject back into the groundwater table, or used for some agricultural purposes.
Target SDGs
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
Target Users (Target Impact Group)
Community, Small and Medium-sized Enterprises, Public Sector Agencies
Distributors / Implementing Organizations
Evoqua Water Technologies; Aqua-Aerobic Systems, Inc.; Bluevita GmbH & Co. KG; Enta Treatment Systems
Competitive Landscape
Direct competitors include AnoxKaldnes Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor and Membrane Biofilm Reactor.
Regions
Europe, North America
Countries
India
Manufacturing/Building Method
Unknown
Intellectural Property Type
Open-source
User Provision Model
Direct sales from local manufacturers.
Distributions to Date Status
Over 1300 plants have operated.
Flow rate (L/min)
16000 L/min
Power Supply Type
Electrical
Technology type
aerobic treatment, activated sludge
BOD Removal Efficiency
95%
COD removal efficiency
90%
NH4-N Removal Efficiency
90%
TSS removal efficiency
95%
Total Phosphorus Removal Efficiency
90%
Fecal Coliform Removal Efficiency
96%
Design Specifications
The SBR tank is designed to add oxygen to wastewater, which enables bacteria to oxidize the organic matter. Once aeration stops, sludge settles in the tank. After settling the sludge and water is separated, and the effluent continues to flow through the system. In most situations, plants are designed with at least two connected SBR to allow for continual wastewater processing.
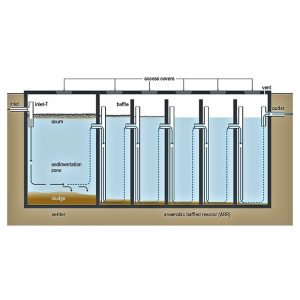
A diagram for the SBR illustrates the processes involved in wastewater treatment.
The SBR operates in two stages in the schematic: during aeration and during settling.
Technical Support
The SBR systems require continuous control by operators. Manufacturers provide technical support and operation training for operators.
Replacement Components
Replacement components can be purchased directly from manufacturers.
Lifecycle
Unknown
Manufacturer Specified Performance Parameters
SBR were developed to require minimal land, produce effluent of high quality, operate completely automated, and be resistant against shock-loads.
Vetted Performance Status
Unknown
Safety
Precautions must be taken during operation to ensure that operators do not come into unsanitary contact with the wastewater or sludge.
Complementary Technical Systems
This treatment system must be coupled with water distribution systems to transport the influent and effluent wastewater to and from the reactor. In addition depending on the desired application of the treated wastewater, further treatment might be required.
Academic Research and References
Strous, M., Heijnen, J., Kuenen, J. & Jetten, M,1998, The sequencing batch reactor as a powerful tool for the study of slowly growing anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing microorganisms. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 50: 589-596
Wang, L., Li, Y., 2009, Sequencing Batch Reactors. Biological Treatment Processes 8: 459-511
Morgenroth, E. et. al., 1997, Aerobic granular sludge in a sequencing batch reactor. Water Research 31 (12): 3191-3194
Zeng, R., Lemaire, R., Yuan, Z. & Keller, J., 2003, Simultaneous nitrification, denitrification, and phosphorus removal in a lab-scale sequencing batch reactor. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 84(2): 170-178
New England Interstate Water Pollution Control Comission, 2005, Sequencing Batch Reactor Design and Operational Considerations.
Ganjidoust, H., Ayati B., 2004, Use of Sequencing Batch Reactors (SBRS) in treatment of wood fiber wastewater, Environmental Science
Wang, D-B. et al., 2008, Biological phosphorus removal in sequencing batch reactor with single-stage oxic process, Bioresoruce Technology 99(13): 5466-5473
NG, J.W. et al., 1993, Fate of coliforms and coliphages in the sequencing batch reactor (SBR), Bioresource Technology 46(3): 197-205
Goal 6. Available: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal6
Compliance with regulations
Unknown
Evaluation methods
The systems are evaluated visually to ensure that each tank proceeds through the five treatment stages: fill, react, settle, decant, and idle.
Other Information
Factsheet - Sequence Batch Reactor (SBR)

Agriculture
August 15, 2024
Implemented by
EAWAG

Agriculture
August 15, 2024
Implemented by
AnoxKaldnes

Agriculture
January 12, 2024
Agriculture
August 16, 2024

Agriculture
June 23, 2024
Implemented by
LoooP Creative Ltd

Agriculture
January 10, 2024
Implemented by
NRSRelief

Agriculture
January 22, 2024
Implemented by
Sanivation

Agriculture
December 13, 2023
Implemented by
change: Water

Agriculture
December 27, 2023
Implemented by
Nippon Basic Co. Ltd.

Agriculture
January 8, 2024
Implemented by
Gadgil Lab, University of California Berkeley
Have thoughts on how we can improve?
Give Us Feedback