
Agriculture
February 26, 2024
AECT Impact 2001A Compressed Earth Block Machine
Read SolutionImplemented by
Advanced Earthen Construction Technologies (AECT)

Updated on February 29, 2024
·Created on August 5, 2017
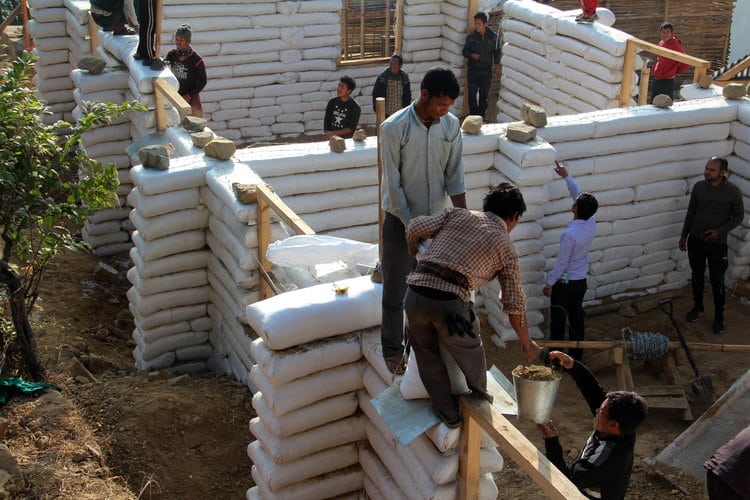
Wall system made with stacked polypropylene bags filled with soil and adhered using barbed wire as mortar.
Good Earth Global (previously Good Earth Nepal) employs and promotes Earthbag technology and other sustainable building methods and teaches these methods to others. Using earthbag construction they work with villagers in developing countries to build disaster-resistant, affordable and eco-friendly homes and schools, and teach an emerging class of builders, architects, and engineers to build with safety and sustainability considerations.
Earthbag technology is a wall system, with structures composed primarily of ordinary soil found at the construction site. The soil is stuffed inside polypropylene bags, which are then staggered like masonry and solidly tamped. Barbed wire is used between the layers of bags and serves as mortar. For seismically active zones, reinforcements like buttresses, vertical rebars and bond beams are recommended. The classical foundation used in earthbag construction is a rubble trench foundation. The roof design can be by preference, as long as it is lightweight.
*Please note that building designs are being included as “products” in the Habitat Sector of the Solutions Library to allow readers to learn from how projects were designed and constructed and how they are serving the occupants, whether effective or ineffective.
Target Users (Target Impact Group)
Distributors / Implementing Organizations
Manufacturing/Building Method
Polypropylene bags, barbed wire, rebar, and sand and cement mix are purchased elsewhere and brought to site. The earth used in the bags and the rubble for the foundation are found on the site.
Intellectural Property Type
Select Type
User Provision Model
Good Earth Global offers programs that include:
Training and education: Standard 7-day workshops, private workshops, on-site training, lectures and presentations, conferences and exhibitions.
Service trips: Construction trips for schools, universities, and building professionals.
Build with them: Good Earth Nepal offers services for the design and management of Earthbag projects and can include everything from conducting site surveys and evaluation, performing cost and budget estimates, meeting with the community and obtaining commitments for required labor and support, designing structures, purchasing equipment and supplies from local merchants, hiring local laborers, establishing a worksite and accommodating volunteers and interns, managing and supervising the construction, and safety inspection.
Other services offered in the program include volunteering and internship, research and development, and advocacy and government relations.
Good Earth Global has a collection of detailed drawings for Earthbag buildings that are freely available upon request.
Distributions to Date Status
Good Earth Global has completed more than thirty Earthbag designs for houses as well as designs for schools for specific geographical requirements. Thirty four Earthbag projects are outlined on the Good Earth Global website.
Unique Design (Yes/No)
No
Intended number of occupants (#)
5-10 occupants
Duration of construction (days)
Varies depending on selected design
Footprint area (m²)
Varies depending on selected design
Number of storeys
1-2 storeys
Material composition
Foundation is made of dry stone masonry, primary material for walls is soil stuffed in polypropylene bags reinforced with vertical rebars and barbed wire. Door and window frames made of wood. Upper perimeter lintel made of reinforced concrete. The roof structure is composed of wood trusses corrugated metal roof panels.
Flammable flash point temperature (ºC)
Soil is fireproof
Thermal insulating capacity (m²*K/W)
Maximum wind speed (km/h)
Unknown
Structural Occupancy Category
II
Seismic Design Category
Suitable Climates
All climates
Design Specifications
The main building materials are soil, polypropylene bags or tubes, and barbed wire. Components that can be added to make a building more earthquake resistant include a rubble trench foundation, thick walls (16 - 19 in.), concrete bond beams, and reinforcements that include vertical rebars, buttresses, and corner reinforcement.
Detailed specifications can be found in the article Earthbag Technology - Simple, Safe and Sustainable, by Dr. Owen Geiger, Director of the Geiger Research Institute of Sustainable Building, and Kateryna Zemskova, Co-Founder and President of Good Earth Nepal. The article was published in the Nepal Engineer's Association Technical Journal.
Technical Support
Technical support can be provided by builders who Good Earth Global has trained in Earthbag construction.
Replacement Components
It is unlikely that repairs are needed (see Lifecycle section), however additional bags and other required materials can be purchased separately should sections of a structure need to be rebuilt.
Lifecycle
Though the full lifespan is unknown, some of the earliest Earthbag structures, such as those constructed by Nader Khalili, founder of CalEarth, have been standing for 20 years. An estimated 55 Earthbag structures built in Nepal survived the 2015 earthquake.
Manufacturer Specified Performance Parameters
Performance targets include safety, ease of construction, reduced use of materials, reduced use of fuel and transportation, less pollution, and cost effective.
Vetted Performance Status
Structural engineers reviewed the standard earth bag designs submitted to the government of Nepal. Earthbags are now included in the building code. Although Good Earth Nepal has not had the resources to conduct a shake table test, 55 Earthbag buildings withstood the 2015 Nepal earthquake.Interview with representative
Safety
Workers are subject to the general dangers of a construction site such as working from heights and with sharp tools. Earth bag construction does not require the operation of any large machinery.
Complementary Technical Systems
Complementary technical systems include earthen flooring, wood frame with slate tiles or corrugated metal panel roofing, or HyPar thin shell concrete roof.
Academic Research and References
Croft C., and Heath A., 2011, Structural Resistance of Earthbag Housing Subjected to Horizontal Loading, University of Bath, Department of Architecture and Civil Engineering, Somerset, United Kingdom.
Geiger O., 2015, Earthbag Building Guide: Abridged and Adapted for Builders, Osho Tapoban Publications.
Kaki H., and Kiffmeyer D., 2004, Earthbag Building: The Tools, Tricks and Techniques, New Society Publishers, British Columbia, Canada.
Vadgama N., and Heath A., 2010, A Material and Structural Analysis of Earthbag Housing, University of Bath, Department of Architecture and Civil Engineering, Somerset, United Kingdom.
Compliance with regulations
Good Earth Global's Earthbag design and protocols have been approved and published by Nepali Federal Government, Department of Urban Development and Building Construction (DUDBC).

Agriculture
February 26, 2024
Implemented by
Advanced Earthen Construction Technologies (AECT)

Agriculture
September 4, 2024

Agriculture
March 8, 2024
Agriculture
June 21, 2024

Agriculture
February 23, 2024
Implemented by
Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA)

Agriculture
February 21, 2024
Implemented by
Global Alliance for Disaster Risk Reduction & Resilience in the Education Sector

Agriculture
February 23, 2024
Implemented by
Bridges to Prosperity
Agriculture
February 23, 2024
Implemented by
Habitat for Humanity

Agriculture
February 21, 2024
Implemented by
Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA)

Agriculture
February 5, 2024
Implemented by
Sisu Global
Have thoughts on how we can improve?
Give Us Feedback
Interesting solution, some concern about vertical reinforcement being necessary for seismic and hurricane application getting lost — shown in some drawings not others. All in all, a lot of good technical information and by highlighting the building material in the context of the application — post disaster and developing country small scale housing, makes a strong case for engineers and architects visiting the site to consider the material in their work.