
Agriculture
January 11, 2024
Caminos de Agua Ceramic filters
Read SolutionImplemented by
Caminos de Agua
 discontinued
discontinued
Updated on January 2, 2024
·Created on August 27, 2015
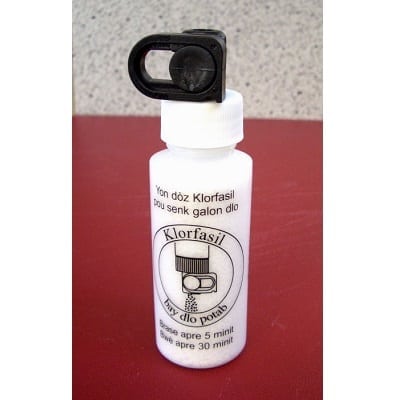
Klorfasil is a locally produced granulated chlorine solution for treating water.
Klorfasil is a locally produced chlorination product for drinking water treatment in rural Haiti. This NGO (also named Klorfasil) sells granulated chlorine, sodium dichloroisocyanurate dihydrate (NaDCC), for disinfection. Klorfasil is intended for household use to reduce transmission of water-borne disease and incidences of diarrhoea.
Target SDGs
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-Being
Market Suggested Retail Price
$10.00
Target Users (Target Impact Group)
Household
Distributors / Implementing Organizations
Klorfasil
Competitive Landscape
Direct competitors include Gadyen Dlo.
Countries
Haiti
Manufacturing/Building Method
Klorfasil dispensers are assembled by hand in Haiti. Interview with representative
Intellectural Property Type
Select Type
User Provision Model
Donations are generally distributed by Klorfasil in sponsorship or association with some other organisations. Interview with representative
Distributions to Date Status
As of January 2012, over 22,000 units have been deployed.
Active Chemical and concentration (%)
Sodium dichloroisocyanurate dihydrate, NaDCC (56%)
Form
Granulated
Dosing method: Batch or flow-through
Batch
Dosing method: Automatic or manual
Manual
Dosing quantity
Based on NTU; if 10 NTU, use 2 doses
Contact time (min)
30 min
Target free disinfectant residual (mg/L)
2 mg/L
Bacteria reduction
Unknown
Virus reduction
Unknown
Protozoa reduction
Unknown
Heavy metals and/or arsenic reduction
Unknown
Treatment lifespan (days)
28-56 (for turbid to clear waters, respectively)
Maximum recommended influent turbidity level (NTU)
10 NTU is treatable, change dosage to reflect higher turbidity
Design Specifications
1 ounce bottles, contain 70 mg of granulated chlorine, weigh 45 grams each is enough for treating 20L water. Each bottle is labeled in Haitian Creole, with product composition, volume of water treatable, and instructions. The chemical NaDCC uses hypochlorous acid to disinfect. The compound has been proven for reducing microbial contamination.
Technical Support
Support is provided by Klorfasil Technicians.
Replacement Components
Replacement parts (such as the dosing valve) are readily available, but very unlikely to be needed. Interview with representative
Lifecycle
Can be stored up to 5 years, even in hot/humid tropical climates.
Manufacturer Specified Performance Parameters
1 bottle treats 450 five-gallon buckets of water, totaling to 8,517 liters per bottle.
Vetted Performance Status
“Program technicians in Hinche report greater than 90%+ positive results for active chlorine in program participant households.”-Klorfasil.
Safety
Avoid contact with eyes.
Complementary Technical Systems
Use of filtration methods or products for pretreatment of water before adding klorfasil.
Academic Research and References
Clasen et al., 2006,Sodiumdichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC) tablets as an alternative to sodium hypochlorite for the routine treatment of drinking water at the household level, International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, Volume 209, Issue 2, 17 March 2006, Pages 173-181
Jain et al., 2010, Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate Tablets for Routine Treatment of Household Drinking Water in Periurban Ghana: A Randomized Controlled Trial, Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010 Jan; 82(1): 16–22.
Clasen et al., 2007, Household water treatment using sodium dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC) tablets: a randomized, controlled trial to assess microbiological effectiveness in Bangladesh, Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007 Jan;76(1):187-92.
“U.S. Non-Profit Organization,” Deep Springs International, 27-Jan-2020. Available: https://deepspringsinternational.org/
“Goal 6,” Sdgs.un.org. Available: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal6
A sample of Klorfasil was obtained in Haiti in June 2013. Tufts University is assisting the Haitian MSPP by evaluating this sample and reviewing materials about the product,” Engineeringforchange.org. Available: https://www.engineeringforchange.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/08/klorfasil-english.pdf
“Listing Category Search Page,” Nsf.org. Available: https://info.nsf.org/Certified/PwsChemicals/Listings.asp?Company=4H810&Standard=060
“Water and Wastewater Standards,” Nsf.org. Available: https://www.nsf.org/nsf-standards/standards-portfolio/water-wastewater-standards.
“Details for ACL 60 EUP CHLORINATING GRANULES,” Epa.gov. Available: https://ordspub.epa.gov/ords/pesticides/f?p=PPLS:8:9893004527311::NO::P8_PUID,P8_RINUM:20242,935-41
Compliance with regulations
NSF / ANSI Standard 60: Drinking Water Treatment Chemicals: Klorfasil is not specifically listed as complying, but dozens other companies selling sodium hypochlorite products for drinking water treatment are approved. This certifies that chemicals are safe at the maximum dose and that any impurities are below the maximum allowable limit.
US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Registration: Klorfasil is not registered with the US EPA. Other products that use NaDCC for drinking water treatment are registered, however. For example, the manufacturer Occidental Chemical has had a NaDCC granule product registered for drinking water disinfection since 1996.
World Health Organization (WHO): The World Health Organization does not currently approve products for use to treat drinking water. However, the Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality lists NaDCC tablets as a point-of-use water treatment method commonly used to prevent diarrhea in developing countries and for travellers. Granular NaDCC is not specifically listed, although tabular NaDCC should perform the same as granular NaDCC if applied at the proper dose.
Evaluation methods
The manufacturer tests the disinfected water in safe water storage container using DPD 1 Rapid test tabs, from LaMotte. They fill plastic test tube with 10 mL sample from the water, add DPD tablet, cap tube and shake gently. DPD tab will turn red in the presence of free chlorine; Klorfasil looks for a 0.5 ppm free chlorine residual after 30 minutes. If no free chlorine residual after 30 minutes, the water source must be changed to something with lower chlorine demand, or a second dose should be used. Interview with representative
Other Information
Project Report to UNICEF on "Assessing the Sustained Uptake Of Selected Point of Use Water Treatment Methods In Emergency Settings" by Clasen and Lantagne (December, 2010)

Agriculture
January 11, 2024
Implemented by
Caminos de Agua

Agriculture
January 17, 2024
Implemented by
Aquagenx

Agriculture
December 29, 2023
Implemented by
LifeStraw

Agriculture
January 3, 2024
Implemented by
Fred Barrett and Dale Andreatta

Agriculture
January 17, 2024
Implemented by
Technorbital

Agriculture
December 27, 2023
Implemented by
Aqus

Agriculture
January 24, 2024
Implemented by
Nanyang Technological University (NTU) Singapore

Agriculture
January 2, 2024
Implemented by
Katadyn Group

Agriculture
January 15, 2024
Implemented by
London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM)
Agriculture
January 19, 2024
Implemented by
SaniTap
Have thoughts on how we can improve?
Give Us Feedback