
Agriculture
January 17, 2024
mWater Field Test Kit
Read SolutionImplemented by
mWater
Updated on February 27, 2024
·Created on March 7, 2022
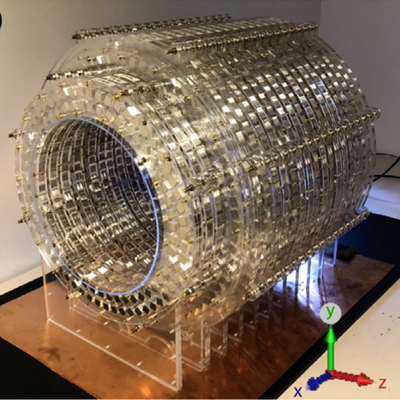
Low-cost MRI system for diagnosis of hydrocephalus in LMIC's
The Low Field MRI Scanner, designed by Dr. Johnes Obungoloch of Mbarara University of Science and Technology, is capable of diagnosing infant hydrocephalus, a frequently occurring condition in sub-Saharan Africa. The system is built using ordinary permanent magnets encompassed in a magnet cylinder as rings adopted as an approach to reduce the cost of design. This low-field technology, which requires a smaller size magnet and yields lower resolution images, weighs 125 kg. As of 2021, this product is still in the prototyping phase.
Target SDGs
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-Being
Market Suggested Retail Price
$18,000.00
Target Users (Target Impact Group)
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises, Public Sector Agencies
Distributors / Implementing Organizations
Unknown
Regions
Africa
Manufacturing/Building Method
This product is currently in the prototyping phase and not yet manufactured at scale. Prototypes are being developed in Uganda by the Biomedical Engineering Department at Mbarara University of Science and Technology.
Intellectural Property Type
Patent
User Provision Model
The designers have not yet selected their user provision model.
Distributions to Date Status
None
Clinical application
Diagnosis of hydrocephalus
Indispensable equipment for function (Yes/No)
Yes
Consumables
None
Device weight (kg)
125 kg
Device dimensions
2264 mm x 1338 mm x 790 mm
Max power consumption (W)
500 W
Power supply type
240 AC supply
Maintenance or calibration required by user at time of use? (Yes/No)
Yes
Type of technology used for test
Permanent Magnet
Time required for procedure
Unknown
Design Specifications
The most expensive part of a conventional MRI system is the superconducting magnets. During the design of a Low Field MRI scanner, the superconducting magnets were replaced by a configuration of inexpensive off-the-shelf permanent magnets placed in a magnet cylinder as rings. The variations in the magnetic field can be used for spatial encoding, thus removing the necessity for gradient coils.
Technical Support
Provided by Biomedical Engineering Research group at Mbarara University.
Replacement Components
Replaceable components include the permanent magnets.
Lifecycle
<10 years Interview with designer in 2021
Manufacturer Specified Performance Parameters
Manufacturer specified performance targets include being less than 50,000 Euros, lightweight, and easy to maintain.
Vetted Performance Status
The research group conducted two forms of the test; 1) performance tests in a lab setting using cabbages and volunteers to carry out brain scans, 2) denoising tests using machine learning algorithms using a two-level Bregman iterative method for image reconstruction and image denoising procedure both in Uganda and Netherlands. Experiments were done on a noisy phantom that was obtained from a low field MRI scanner. Results demonstrated that the two-level Bregman algorithm performs superior image reconstructions that are almost noise-free. The method also performed better than the TBMDU algorithm, which performed better than DLMRI. However, the TBMDU algorithm was faster than the Bregman algorithm due to additional iterations required during the denoising step.
Safety
The low field MRI scanner uses a non-ionizing magnet field which is proven to be the safest technique for medical imaging.
Complementary Technical Systems
The MRI system has been made to configure on tablet/iPad as an alternative interface.
Academic Research and References
Geçmen, D., 2020, “Deep Learning Techniques for Low-Field MRI,” Masters Thesis for TU Delft.
Diehl, J. C., van Doesum, F., Bakker, M., van Gijzen, M., O’Reilly, T., Muhumuza, I., … & Kabachelor, E. M., 2020, “The embodiment of low-field MRI for the diagnosis of infant hydrocephalus in Uganda,” 2020 IEEE Global Humanitarian Technology Conference, GHTC, pp. 1-8.
den Bouter, M. D. L., Gecmen, D., Meijer, A., de Gans, D., Middelplaats, L., Remis, R., & van Gijzen, M. B., 2020, “Description of a Low-field MRI Scanner Based on Permanent Magnets,” CVCS.
den Bouter, M. D. L., van Gijzen, M., & Remis, R., 2021, “Low-field magnetic resonance imaging using multiplicative regularization,” Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 75, pp. 21-33.
Chavali, A. K., Arvind K. Chavali and Ramesh Ramji., 2018, “Frugal Innovation in Bioengineering for the Detection of Infectious Diseases,” pp. 113.
van Doesum, F., 2020, “MRI for Africa: The design of an MRI for the diagnosis of infant hydrocephalus in Ugandan hospitals,” Masters Thesis for TU Delft.
Compliance with regulations
None, as the Low field MRI is still under development.
Evaluation methods
The methods included in-house testing using small phantom images and a pilot with volunteer participants. More studies will be conducted after the completion of the design.
Other Information
None

Agriculture
January 17, 2024
Implemented by
mWater

Agriculture
June 5, 2024
Implemented by
Stamen Design

Agriculture
December 27, 2023
Implemented by
Aquabox, UK

Agriculture
December 18, 2023
Implemented by
Be Girl

Agriculture
January 11, 2024
Implemented by
Kenya Ceramic Project (KCP)

Agriculture
January 8, 2024
Implemented by
DayOne Response
Agriculture
December 19, 2023
Implemented by
Hadleigh Health Technologies and Rice University

Agriculture
February 16, 2024
Implemented by
Eniware

Agriculture
December 19, 2023
Implemented by
GlobalNeoNat
Agriculture
November 17, 2023
Implemented by
AYZH
Have thoughts on how we can improve?
Give Us Feedback