
Agriculture
February 20, 2024
Arktek Passive Vaccine Storage Device
Read SolutionImplemented by
Intellectual Ventures Lab

Updated on September 26, 2024
·Created on July 23, 2019
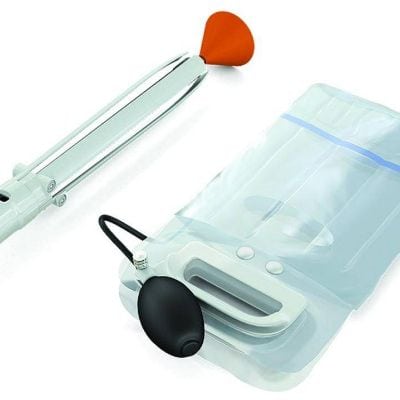
Odon Device is a simple assisted vaginal delivery device for complicated labor
The Odon Device was designed for assistive birth delivery in cases of prolonged labor, transverse, or breech babies. The device, which is currently under clinical trial, is intended to reduce complications from prolonged labor, such as infection, and newborn complications, such as birth asphyxia.
Target Regions
Africa, Central Asia, East Asia, East Asia and Pacific, North Asia, South America, South Asia, Southeast Asia
Target SDGs
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-Being
Market Suggested Retail Price
$50.00
Target Users (Target Impact Group)
Community, Small and Medium-sized Enterprises
Distributors / Implementing Organizations
WHO, Becton Dickinson and Company
Regions
Africa, Central Asia, East Asia, East Asia and Pacific, North Asia, South America, South Asia, Southeast Asia
Countries
Afghanistan
Manufacturing/Building Method
The Becton Dickinson Company has the rights to manufacture the Odon Device, however, manufacturing has not yet begun.
Intellectural Property Type
Select Type
User Provision Model
Product is not yet available on the market
Distributions to Date Status
None
Clinical application
Prolonged labor
Consumables
None
Training level required
Minimal Device Training required
Anesthetic needed?
None
Type of grip
Handles
Design Specifications
The Odon Device is a vaginal delivery device that employs a circumferential air cuff over the fetal head to perform instrumental vaginal delivery. The product consists of a soft plastic cup that fits around the head of the baby, an inserter that grasps the head, and a polyethylene sleeve that is inflated with air that allows for the guidance of the baby out of the birth canal. A force of up to 19 kg can be applied to aid in the extraction process.
Technical Support
None
Replacement Components
Unknown
Lifecycle
Unknown
Manufacturer Specified Performance Parameters
Performance targets include: low cost, compact dimensions, usable globally, ease of use, safe for both fetus and mother, reduces risk of inoculability between mother and child.
Vetted Performance Status
The WHO Human Reproduction Program supported the evaluation of this product in hospitals in Argentina and South Africa. The device was successfully inserted into 93% of women, and 71% had a successful delivery after one-time application.
Safety
There are risks of mechanical failure while operating, and of maternal or newborn trauma during use.
Complementary Technical Systems
None
Academic Research and References
Requejo, J.H. and Belizán, J.M., 2013, Odon Device: a Promising Tool to Facilitate Vaginal Delivery and Increase Access to Emergency Care, Reproductive Health, 10(1), pp. 42.
World Health Organization Odon Device Research Group, 2013, Feasibility and Safety Study of a New Device (Odón Device) for Assisted Vaginal Deliveries: Study Protocol, Reproductive health, 10(1), pp. 33.
Schvartzman, J., Krupitski, H., Merialdi, M., Betran, A.P. and Requejo, J., 2018, Odon Device for Instrumental Vaginal Deliveries: Results of a Medical Device Pilot Clinical Study, Reproductive health, 15(1), pp. 45.
O’brien, S., Winter, C., Burden, C., Boulvain, M., Draycott, T., and Crofts, J., 2017, Fetal Head Position and Perineal Distension Associated with the Use of the BD Odon Device™ in Operative Vaginal Birth: a Simulation Study, BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, 124, pp. 10–18.
O’brien, S., Mouser, A., Odon, J., Winter, C., Draycott, T., Sumitro, T., Alisantoso, D., Lim, W., Merialdi, M., Stankovic, A., et al, 2017, Design and Development of the BD Odon DeviceTM: a Human Factors Evaluation Process, BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, 124, pp. 35–43.
O’brien, S., Winter, C., Burden, C., Boulvain, M., Draycott, T., and Crofts, J., 2017, Pressure and Traction on a Model Fetal Head and Neck Associated with the use of Forceps, Kiwi™ Ventouse and the BD Odon Device™ in Operative Vaginal Birth: a Simulation Study, BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, 124, pp. 19–25.
Compliance with regulations
The device has not been approved for use in the US but has been evaluated by the WHO, which found that the device was feasible but will require a randomized-controlled trial to evaluate effectiveness and safety compared to other accepted methods.

Agriculture
February 20, 2024
Implemented by
Intellectual Ventures Lab
Agriculture
February 21, 2024
Implemented by
Equalize Health

Agriculture
March 10, 2024
Implemented by
Disease Diagnostic Group
Agriculture
February 8, 2024
Implemented by
Design That Matters (DtM)

Agriculture
January 3, 2024
Implemented by
Stanford Researchers and the International Centre for Diarrhoeal Disease Research, Bangladesh

Agriculture
February 5, 2024
Implemented by
Circ MedTech
Agriculture
November 24, 2023
Implemented by
Hadleigh Health Technologies, and Rice 360
Agriculture
December 12, 2023
Implemented by
Sohum Innovation lab
Agriculture
December 19, 2023
Implemented by
Star Syringe

Agriculture
February 26, 2024
Implemented by
Hemex Health
Have thoughts on how we can improve?
Give Us Feedback